What Is Equity?
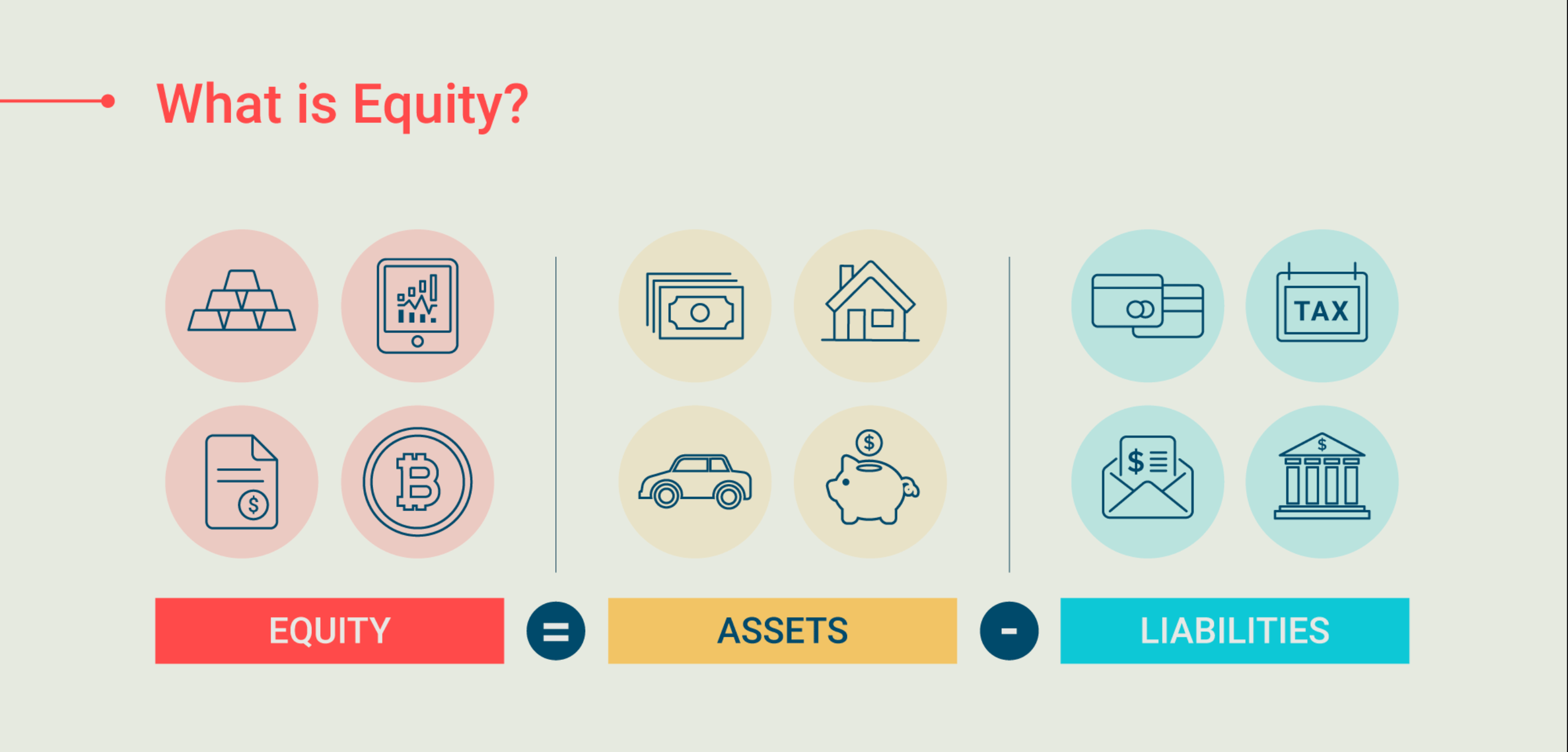
Equity, also known as shareholders' equity or owners' equity for privately held businesses, is the sum of money that would remain in the hands of a company's shareholders in the event that all of its assets were sold off and its liabilities were fully settled. In the event of an acquisition, it is the sales value of the business less any debts that were not transferred along with the transaction.
Additionally, a company's book value may be represented by shareholder equity. In certain cases, equity may be provided as payment-in-kind. Additionally, it symbolizes the proportionate ownership of a company's stock.
Equity is a component of a firm's
balance sheet and is one of the most often used metrics by analysts to evaluate the financial standing of a company.
KEY KNOWLEDGE
How does Shareholder's Equity Works ?
Investors and analysts can easily understand a business's financial situation by using the "assets-minus-liabilities" shareholder equity calculation, which compares actual statistics that show everything the company has and everything it owes. Equity is defined as a company's capital that is raised and then utilized to fund operations, invest in projects, and buy assets. Generally, a company can raise money by issuing bonds or debt (loans) or equity (stock sales). Equity investments are typically sought after by investors because they offer a larger chance to participate in a company's growth and earnings.
Equity is significant because it expresses, in terms of the percentage of a company's shares, the value of an investor's interest in the business. Shareholders have the opportunity to receive dividends and capital gains when they own firm shares. Possession of equity entitles shareholders to vote on decisions made by the company and board of director elections. The benefits of equity ownership encourage shareholders' continued involvement in the business.
Formula and How to Calculate Shareholders' Equity
The equity of a company may be calculated using the following formula, which comes from the accounting equation:
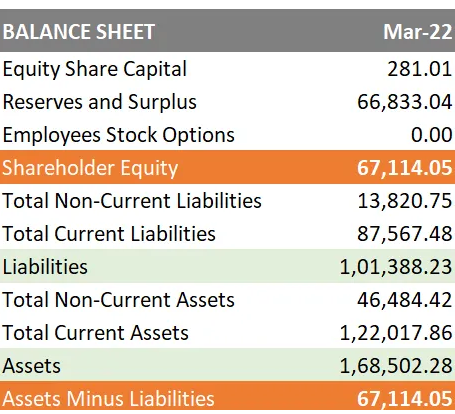
Shareholders’ Equity=Total Assets−Total Liabilities
A company's share capital and retained earnings less the value of its treasury shares can also be used to calculate shareholder equity. But this approach is less typical. The usage of total assets and total liabilities is more indicative of a company's financial health, even if both approaches provide the same exact number.
Components of Shareholder's Equity :
The portion of net earnings that were not distributed as dividends to shareholders is known as retained earnings, and it is a component of shareholder equity. Retained earnings are essentially savings since they are the total of all profits that have been set aside or preserved for later use. As long as the business keeps reinvesting a percentage of its profits, retained earnings increase.
Retained profits have the potential to surpass the amount of equity capital given by investors at some time. In most cases, retained earnings make up the majority of investors' equity in long-running businesses.
Calculation of Shareholder's Equity