INVESTMENTS
HEDGE MUTUAL FUND
What is Hedge Fund ?
A hedge fund is a limited partnership made up of private investors whose capital is overseen by qualified fund managers. These managers employ a variety of techniques, such as trading non-traditional assets or using leverage, to generate returns on investments that are higher than average.
Investing in hedge funds, which frequently target rich customers, is seen as a dangerous alternative investing option that typically demands a large minimum commitment or net worth.
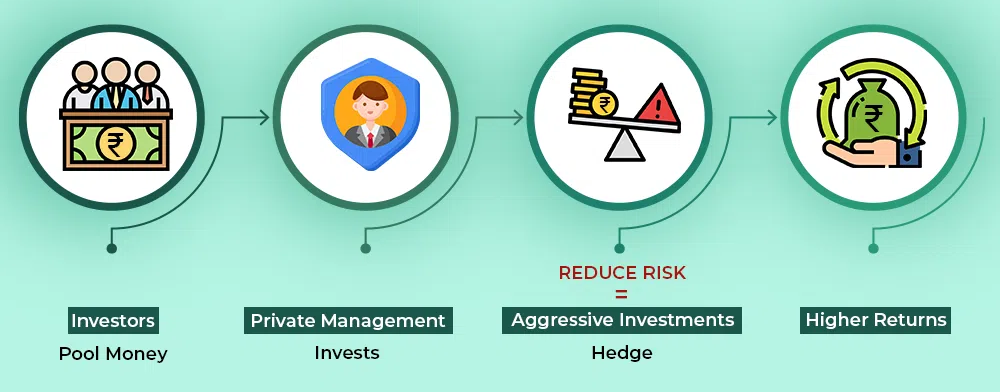
Asset classes including derivatives, stocks, bonds, currencies, and convertible securities make up a hedge fund portfolio. They are therefore seen as alternative investments as well. They require active management since they are an asset class that aims to "hedge" investor capital against market ups and downs. In contrast to the normal stock mutual fund, they frequently use high levels of leverage. They own stakes in listed and unlisted derivatives, as well as long and short positions.
KEY KNOWLEDGE
What are the Features of Hedge Fund
Hedged fund investments are restricted to accredited or qualified investors only. High net worth individuals (HNIs), banks, insurance providers, endowments, and pension funds make up the majority of them. Investing in these funds requires a minimum ticket size of Rs 1 crore.
A wide variety of investments, including bonds, stocks, real estate, currencies, and derivatives, are held by hedge funds. Indeed, they must encompass all asset types that are restricted by the mandate.
They both work with the notions of management fee and spending ratio. It is known as "Two and Twenty" globally, denoting a set charge of 2% and a profit share of 20%. In India, the management fee for hedge funds can be as little as 1% to less than 2%. Additionally, profit sharing typically ranges from 10% to 15%.
Investing in hedge funds exposes money to significant losses. Generally speaking, investment lock-in periods are somewhat lengthy. These funds' use of leverage has the potential to significantly reduce investment returns.
Hedge funds classified as Category III AIFs are still not eligible for tax pass-through status. This suggests that these funds' income is subject to investment fund taxation. Therefore, the unit holders will not be responsible for the tax liability. The fact that they are not competing on an even playing field with other mutual funds is a disadvantage for this sector.
How do Hedge Fund Works ?
Hedge fund returns are not a reflection of the state of the market, but rather of the fund manager's ability. Despite market fluctuations, the asset managers here try their utmost to minimize or eliminate market risk and provide strong returns. They operate in niche markets to increase diversity and lower risks.
Here, the management can sell shares to be repurchased at a lower price in the future by expecting that prices would decline.
Inconsistent or ineffective pricing may occasionally be seen in the securities. Supervisors take advantage of this.
Certain corporations that are experiencing financial strain or may potentially become insolvent may offer their securities for incredibly low prices. After considering the options, the management could choose to purchase.
Types of Hedge Fund:
Global Macro Hedge Fund :
Actively managed funds known as global macro hedge funds try to make money off of large market fluctuations brought on by political or economic developments.
Example : Citadel, Bridgewater Associates, AQR Capital Management.
Equity Hedge Fund:
An equity hedge fund might be national or international in scope, investing in profitable stocks and using stock index or stock shorting to protect against equity market declines.
Relative Value Hedge Fund:
A relative value hedge fund looks to take advantage of spread or price inefficiencies by short-term variations in the prices of linked assets.
How do hedge Fund makes Money ?
Through his business, A.W. Jones & Co., Australian financier Alfred Winslow Jones is credited with founding the first hedge fund in 1949. With the money he raised, he created the long/short equities model, a fund that uses short selling to reduce the risk associated with long-term stock trading.
As the first money manager to mix leverage, short selling, and performance-based remuneration, Jones changed his fund to a limited partnership in 1952 and added a 20% incentive fee for the managing partner.
Because the management fee is determined by the net asset value of each investor's shares, a $1 million investment would result in a $20,000 management fee for that year, which would go toward funding the hedge fund's operations and paying the fund manager.
The performance fee is commonly 20% of profits. If an investment of $1 million increases to $1.2 million in one year, $40,000 is the fee owed to the fund.
Hedge Fund Strategies :
The four main categories into which hedge fund strategies are often divided are global macro, directional, event-driven, and relative value (arbitrage). Each of these groups' strategies has a unique risk and return profile. For flexibility, risk control, or diversification, a fund may use one strategy or several strategies. The offering memorandum, sometimes referred to as the prospectus for a hedge fund, provides prospective investors with details on the firm's investing strategy, investment type, and maximum leverage.
The way a hedge fund approaches the market, the specific instruments it uses, the industry the fund focuses in (such as healthcare), the process it uses to choose assets, and the degree of diversity it has inside the fund are all components of a hedge fund strategy. various asset types, such as equities, fixed income, commodities, and currencies, are viewed differently by various markets. Equities, fixed income, futures, options, and swaps are among the instruments employed. There are two types of strategies: "discretionary/qualitative" strategies, where managers choose the investments, and "systematic/quantitative" strategies, where computer systems choose the investments.
An event-driven hedge fund strategy takes advantage of temporary stock mispricing, spawned by corporate events like restructurings, mergers and acquisitions, bankruptcy, or takeovers.
Difference between Hedge Fund vs Mutual Fund
| Basics | Hedge Fund | Mutual Fund |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | A hedge fund is a collection of investments made by a few select wealthy people who combine their funds to buy assets. | Mutual funds are trusts wherein the combined assets of several participants are used to affordably buy a diverse assortment of securities. |
| Return | Return is Absolute | Return is Relative |
| oversight | Aggressively | Less Aggressively |
| Owner | Few Owners | Thousand of Owners |
| Type | Pension funds, endowment funds, and high-net-worth individuals | Retail investors are the investor of mutual funds. |
| Control | Less regulations | Regulated by SEBI |
Frequently Asked Questions
High profits are rarely certain. The majority of hedge funds make investments in the same assets that ordinary investors and mutual funds may buy. Therefore, the only way you can reasonably expect larger returns is if you choose a timely approach or a superior management.
Investors in a 3(c)(1) hedge fund may number up to 99. Although some funds may decide to allow up to 35 non-accredited participants, these individuals will often need to be "accredited investors."
Related Articles :